This document provides instructions on how to configure role access capabilities to users in WordPress.
WordPress provides the website owner the ability to control what users can do within the site. This is done by assigning users within the site with a role. These roles control what tasks can be controlled in the WordPress CMS. Everything from editing a page to the ability to posting a comment.
WordPress does a good job defining the default roles like this:
- Super Admin – somebody with access to the site network administration features and all other features. See the Create a Network article. (Typically, you only see the Super Admin option when a multi-site is enacted.)
- Administrator (slug: ‘administrator’) – somebody who has access to all the administration features within a single site.
- Editor (slug: ‘editor’) – somebody who can publish and manage posts including the posts of other users.
- Author (slug: ‘author’) – somebody who can publish and manage their own posts.
- Contributor (slug: ‘contributor’) – somebody who can write and manage their own posts but cannot publish them.
- Subscriber (slug: ‘subscriber’) – somebody who can only manage their profile.
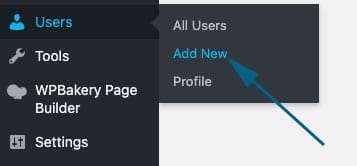
To add a new user, select ‘Add User’ from the WordPress Dashboard menu on the left side.
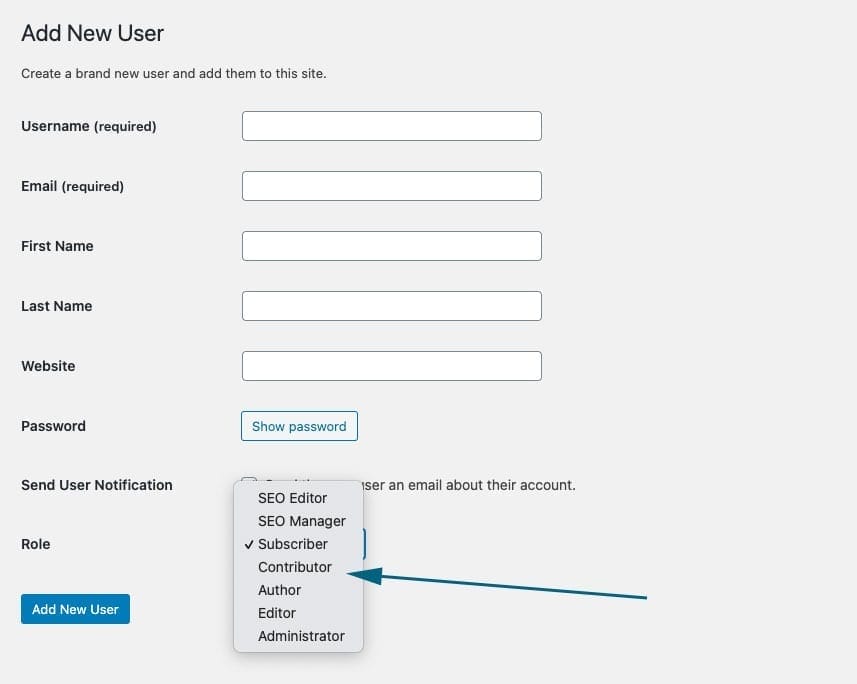
At a minimum, add a ‘Username’ and ‘Email’ address (both are required). It is best practice to also add the ‘First Name’ and ‘Last Name’ as this will be used on news posts and commenting entries.
The last dropdown field is ‘Role’. By default, it is set to ‘Subscriber’ which is limited access. Set the role that is appropriate for the user and press ‘Add New User’ to save the profile.
Please email us if you have any problems or ideas to improve these instructions.









